Software Overview
ROBOTIS Hand is a dexterous robotic hand system designed for real-world Physical AI research and manipulation tasks. It supports high-DOF finger control and enables smooth integration of both teleoperation and AI policy execution.
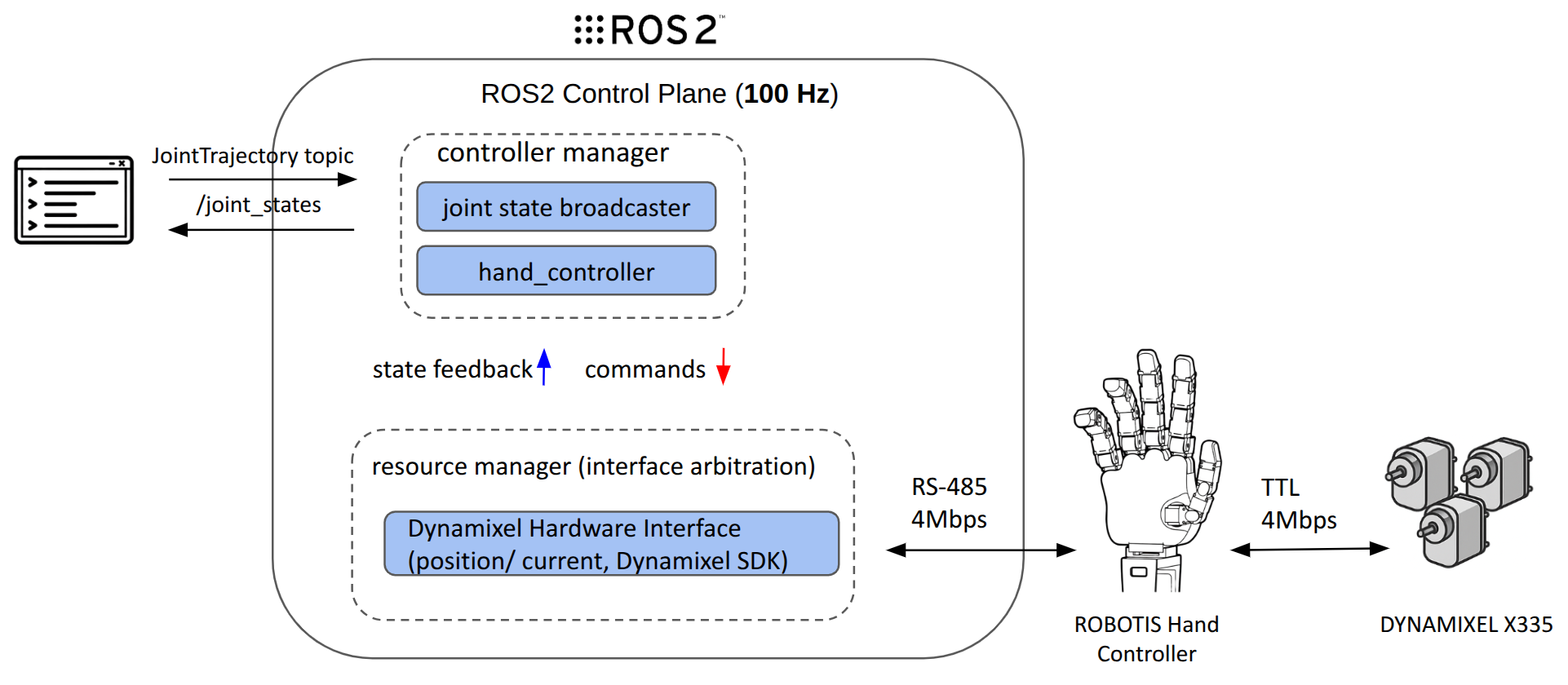
The platform runs on ROS 2 Jazzy and uses the ros2_control framework for real-time joint-level control. Each hand features 20 degrees of freedom powered by XM335 actuators operating in position mode via TTL communication. The actuators are connected through a Hand Controller Board that converts RS-485 signals from the U2D2 interface to 5 TTL channels, enabling distributed control of finger joints. The system also integrates tactile sensors that provide feedback through ros2_control state interfaces, enabling rich sensory perception for manipulation tasks.
This platform is designed for:
- Collecting motion data through teleoperation
- Training reinforcement learning or imitation learning models
- Running AI-generated trajectories in real time without changing system code
It is suitable for researchers, developers, and integrators working with AI-enabled robotics.
System Architecture
The diagram below illustrates the overall control structure of ROBOTIS Hand.
External teleoperation or trajectory commands are received via ROS 2 topics, processed in real time by
ros2_control, and executed by DYNAMIXEL Actuators via TTL.
| Layer | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Control | ros2_control | 100Hz joint control loop |
| Actuators | XM335 | Position mode via TTL |
| Hand Controller Board | PCB Board (RS-485) | RS-485 to 5 TTL channels |
| Communication | U2D2 (RS‑485) | 4 Mbps, Dynamixel Protocol 2.0 |
| Sensors | Tactile sensors | Read via ros2_control state_interfaces |
Why ros2_control?
ros2_control is a real-time, modular control framework used in ROS 2. ROBOTIS Hand uses it without major changes.
- Separates control logic from hardware drivers
- Operates at a fixed 100Hz update rate
- Supports dynamic loading or replacement of controllers
- Allows AI policies to send trajectory commands using standard ROS topics
This structure supports both manual operation and AI-based control in the same system.
Motion Execution Pipeline
Input Source (Teleoperation)
↓
ROS 2 JointTrajectory Topic
↓
controller_manager (100Hz)
↓
JointTrajectoryController(s)
↓
resource_manager (interface arbitration)
↓
DynamixelHardwareInterface (position / current)
↓
RS‑485 via Dynamixel SDK
↓
DYNAMIXEL ActuatorsStep-by-Step
- Trajectory generation — Created by VR, GUI, or AI model
- ROS topic publishing — Commands sent to
/leader/joint_trajectory_command_broadcaster_* - Controller manager — Runs the main
read → update → writeloop at 100Hz - JointTrajectoryController — Splits trajectory and commands each joint
- Resource manager — Controls access to command interfaces and prevents conflicts between controllers
- Hardware interface — Converts commands to RS-485 packets using Dynamixel SDK
- Actuators — Execute the motion and return position/current feedback
Controller Configuration & Joint Mapping
| Controller | Segment | DOF | Input Topic |
|---|---|---|---|
hand_l_controller | Left hand | 20 | /leader/joint_trajectory_command_broadcaster_left_hand/joint_trajectory |
hand_r_controller | Right hand | 20 | /leader/joint_trajectory_command_broadcaster_right_hand/joint_trajectory |
joint_state_broadcaster | All joints | – | Publishes to /joint_states |
All controllers (except joint_state_broadcaster) use the JointTrajectoryController type.
By default, all joints operate in position mode.
Controller YAML Example (link)
/**:
controller_manager:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: False
update_rate: 100 # Hz
joint_state_broadcaster:
type: joint_state_broadcaster/JointStateBroadcaster
left_hand_controller:
type: joint_trajectory_controller/JointTrajectoryController
right_hand_controller:
type: joint_trajectory_controller/JointTrajectoryController
left_effort_controller:
type: effort_controllers/JointGroupEffortController
right_effort_controller:
type: effort_controllers/JointGroupEffortController
/**:
left_hand_controller:
ros__parameters:
joints:
- finger_l_joint1
- finger_l_joint2
- finger_l_joint3
- finger_l_joint4
- finger_l_joint5
- finger_l_joint6
- finger_l_joint7
- finger_l_joint8
- finger_l_joint9
- finger_l_joint10
- finger_l_joint11
- finger_l_joint12
- finger_l_joint13
- finger_l_joint14
- finger_l_joint15
- finger_l_joint16
- finger_l_joint17
- finger_l_joint18
- finger_l_joint19
- finger_l_joint20
command_interfaces:
- position
state_interfaces:
- position
- velocity
allow_nonzero_velocity_at_trajectory_end: true
allow_partial_joints_goal: true
/**:
right_hand_controller:
ros__parameters:
joints:
- finger_r_joint1
- finger_r_joint2
- finger_r_joint3
- finger_r_joint4
- finger_r_joint5
- finger_r_joint6
- finger_r_joint7
- finger_r_joint8
- finger_r_joint9
- finger_r_joint10
- finger_r_joint11
- finger_r_joint12
- finger_r_joint13
- finger_r_joint14
- finger_r_joint15
- finger_r_joint16
- finger_r_joint17
- finger_r_joint18
- finger_r_joint19
- finger_r_joint20
command_interfaces:
- position
state_interfaces:
- position
- velocity
allow_nonzero_velocity_at_trajectory_end: true
allow_partial_joints_goal: true
/**:
left_effort_controller:
ros__parameters:
joints:
- finger_l_joint1
- finger_l_joint2
- finger_l_joint3
- finger_l_joint4
- finger_l_joint5
- finger_l_joint6
- finger_l_joint7
- finger_l_joint8
- finger_l_joint9
- finger_l_joint10
- finger_l_joint11
- finger_l_joint12
- finger_l_joint13
- finger_l_joint14
- finger_l_joint15
- finger_l_joint16
- finger_l_joint17
- finger_l_joint18
- finger_l_joint19
- finger_l_joint20
/**:
right_effort_controller:
ros__parameters:
joints:
- finger_r_joint1
- finger_r_joint2
- finger_r_joint3
- finger_r_joint4
- finger_r_joint5
- finger_r_joint6
- finger_r_joint7
- finger_r_joint8
- finger_r_joint9
- finger_r_joint10
- finger_r_joint11
- finger_r_joint12
- finger_r_joint13
- finger_r_joint14
- finger_r_joint15
- finger_r_joint16
- finger_r_joint17
- finger_r_joint18
- finger_r_joint19
- finger_r_joint20Debugging & Visualization Tools
| Tool / Topic | Description |
|---|---|
ros2 control list_controllers | List loaded controllers and their status |
/joint_states | Real-time joint position and velocity feedback |
| RViz2 | 3D view of robot model (URDF), TF, and movement |
Safety & Fault Handling
- Joint limits are enforced using the URDF and controller configuration
- Out-of-range values are clamped by the hardware interface (YAML-defined limits)
- The Dynamixel hardware interface checks for communication errors with each motor